Let’s talk about something that might sound like a math teacher's favorite topic, but trust me, it’s more relatable than you think. Mean, median, and mode – these aren’t just random words tossed around in your high school stats class. They’re like the three musketeers of data, working together to help us understand the world better. Whether you’re analyzing test scores, figuring out income trends, or even trying to win at trivia night, knowing how these concepts connect can save the day. So, buckle up, because we’re diving deep into the mean median mode connections that matter.
Now, you might be wondering, "Why should I care about this?" Well, here's the thing: numbers don’t lie. Or at least, they don’t if you know how to interpret them. The mean, median, and mode are like your trusty tools for making sense of data. They help you figure out what’s normal, what’s average, and what’s popping up more than it should. And in a world where data drives decisions, understanding these connections can give you an edge.
Before we dive deeper, let me set the scene. Imagine you’re at a dinner party, and someone starts talking about averages. You nod politely, but inside, you’re thinking, "What does this have to do with my life?" Turns out, a lot. From calculating your monthly expenses to understanding global trends, mean, median, and mode are your secret weapons. So, let’s break it down and see how they all fit together.
Read also:Simple Strategies To Lose Weight And Feel Great
What Exactly Is Mean Median Mode?
First things first, let’s get our definitions straight. The mean, median, and mode are all measures of central tendency, which is just a fancy way of saying they help you find the center of a data set. Think of them as your compass when you’re lost in a sea of numbers. But what makes each one unique?
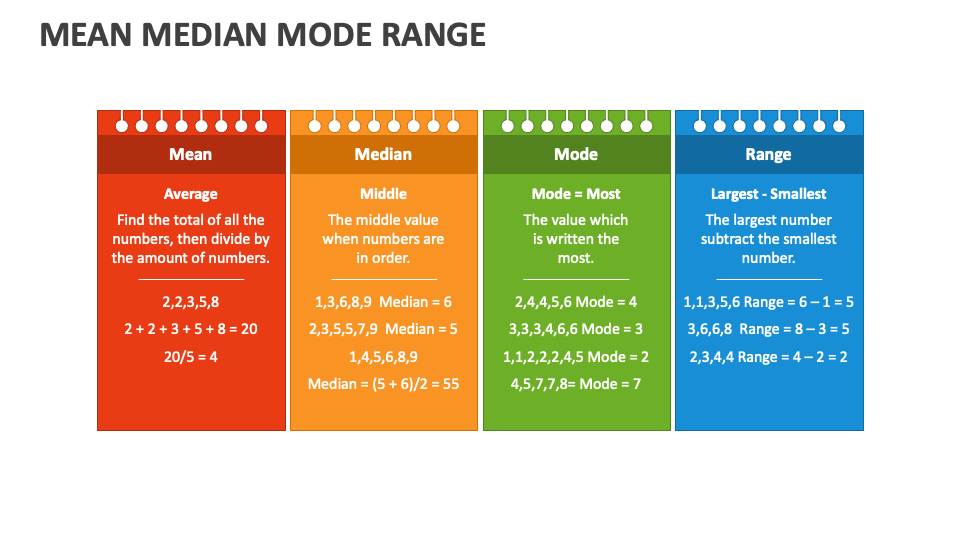
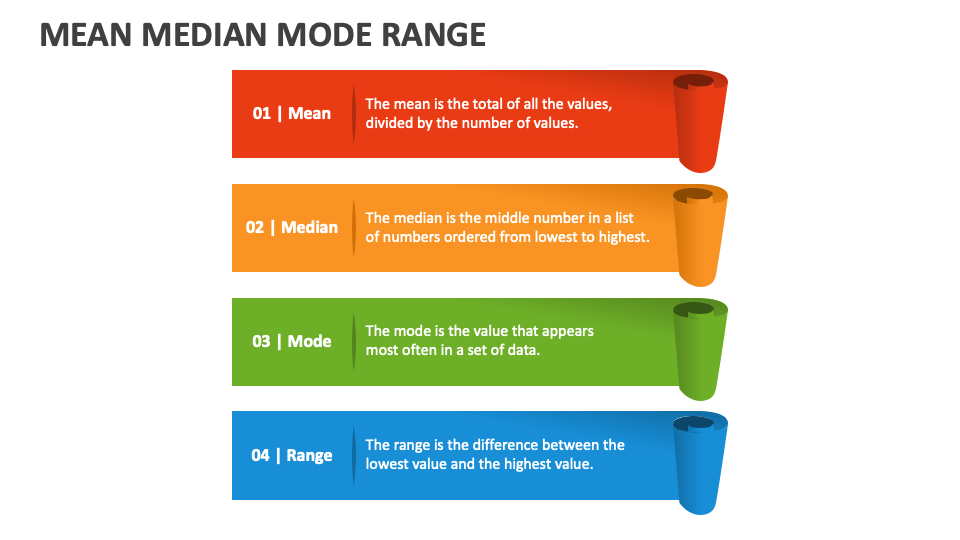
- Mean: This is the one you probably know best. It’s the average of a bunch of numbers. You add them all up and divide by how many there are. Simple, right?
- Median: Now, this one’s a bit different. The median is the middle number in a sorted list. So, if you line up all your numbers from smallest to largest, the one right in the middle is your median.
- Mode: Lastly, we have the mode. This is the number that shows up the most in your data set. If no number repeats, then you don’t have a mode. Easy peasy.
Each of these has its own strengths and weaknesses, and understanding them is key to unlocking their full potential. So, let’s explore how they connect and why it matters.
Why Do Mean Median Mode Connections Matter?
Here’s the deal: when you’re dealing with data, having just one measure isn’t enough. Think about it like this: if you’re trying to describe a person, would you only use their height? Of course not! You’d want to know their weight, age, maybe even their favorite color. Similarly, when analyzing data, you need multiple perspectives to get the full picture.
The mean, median, and mode connections give you a well-rounded view of your data. For example, if you’re looking at income levels in a city, the mean might tell you the average income, but the median will show you what most people actually earn. And the mode? That’ll highlight any income levels that are super common. Together, they paint a clearer picture than any one measure could alone.
When to Use Each Measure
Knowing when to use the mean, median, or mode is like knowing when to use a hammer versus a screwdriver. Each tool has its place, and the same goes for these statistical measures.
Mean: The Go-To Guy
The mean is your default choice when you need an overall average. It’s great for situations where all the data points are equally important. For example, if you’re calculating your GPA or figuring out how much you spend on coffee each month, the mean is your best friend.
Read also:Willie Nelson At 92 Still Touring Making Music And Inspiring Fans
Median: The Middle Child
Sometimes, though, the mean can be misleading. If you have a few really high or really low numbers, they can skew your average. That’s where the median comes in. It’s not affected by extreme values, making it perfect for situations like housing prices or salaries, where a few outliers can throw off the mean.
Mode: The Trendsetter
Finally, we have the mode, which is all about spotting trends. If you’re trying to figure out what’s popular or common, the mode is your go-to. Think about things like favorite ice cream flavors or most-watched TV shows. The mode helps you identify what’s catching on.
Real-Life Applications of Mean Median Mode Connections
Let’s get real for a second. How often do you actually use mean, median, and mode in everyday life? Turns out, more than you think. Here are a few examples:
- Education: Teachers use these measures to analyze test scores and identify areas where students need extra help.
- Business: Companies use them to understand customer preferences and sales trends.
- Healthcare: Doctors and researchers use them to analyze patient data and track disease patterns.
Even if you’re not crunching numbers for a living, understanding these concepts can help you make better decisions. Whether you’re budgeting, investing, or just trying to understand the world around you, mean, median, and mode have got your back.
Common Misconceptions About Mean Median Mode Connections
There are a few myths floating around about these statistical measures, and it’s time to set the record straight.
- Myth 1: The mean is always the best measure. Nope! As we’ve seen, the median and mode have their own strengths.
- Myth 2: You only need one measure to understand your data. Wrong again! Using all three gives you a more complete picture.
- Myth 3: These concepts are only useful for statisticians. Not true! Anyone can benefit from understanding mean, median, and mode.
By clearing up these misconceptions, you’ll be better equipped to use these tools effectively in your own life.
How to Calculate Mean Median Mode Connections
Ready to get your hands dirty? Let’s walk through how to calculate each measure step by step.
Calculating the Mean
Step 1: Add up all your numbers.
Step 2: Divide the total by how many numbers you have.
And just like that, you’ve got your mean!
Calculating the Median
Step 1: Arrange your numbers in order from smallest to largest.
Step 2: Find the number in the middle.
If you have an even number of data points, take the average of the two middle numbers.
Calculating the Mode
Step 1: Look at your data set.
Step 2: Find the number that appears the most.
If no number repeats, there is no mode.
With these steps in your toolkit, you’ll be calculating like a pro in no time.
Case Studies: Mean Median Mode Connections in Action
Let’s look at some real-world examples to see how these concepts play out in practice.
Case Study 1: Analyzing Test Scores
Imagine you’re a teacher trying to understand how your students performed on a recent exam. You calculate the mean to get an overall picture, the median to see what most students scored, and the mode to identify any common scores. Together, these measures help you tailor your teaching to better meet your students’ needs.
Case Study 2: Evaluating Income Levels
In a city where a few wealthy individuals earn significantly more than the rest of the population, the mean income might be misleadingly high. By also considering the median and mode, you can get a more accurate picture of what most people actually earn.
These case studies show how mean, median, and mode connections can provide valuable insights in a variety of contexts.
Tools and Resources for Mastering Mean Median Mode Connections
If you’re ready to take your data analysis skills to the next level, there are plenty of tools and resources available to help you out.
- Spreadsheets: Programs like Excel and Google Sheets make it easy to calculate mean, median, and mode with built-in functions.
- Statistical Software: Tools like R and Python offer more advanced capabilities for analyzing large data sets.
- Online Calculators: If you’re just starting out, there are plenty of free online calculators that can help you crunch the numbers.
With the right tools, mastering mean, median, and mode connections is easier than ever.
Challenges and Limitations of Mean Median Mode Connections
While these measures are incredibly useful, they’re not without their limitations. For example, the mean can be skewed by outliers, the median might not reflect the overall trend, and the mode might not exist in some data sets. It’s important to be aware of these challenges and use these measures in combination with other tools to get the most accurate results.
Conclusion: Why Mean Median Mode Connections Are Essential
In conclusion, understanding mean, median, and mode connections is more than just a math lesson. It’s a powerful skill that can help you make sense of the world around you. By using these measures together, you can gain deeper insights into data and make more informed decisions.
So, what’s next? Start practicing! Whether you’re analyzing your own data or just trying to impress your friends at trivia night, mean, median, and mode are your new best friends. And don’t forget to share this article with anyone who needs a crash course in data analysis. Together, let’s make the world a more number-savvy place!
Table of Contents
- What Exactly Is Mean Median Mode?
- Why Do Mean Median Mode Connections Matter?
- When to Use Each Measure
- Real-Life Applications of Mean Median Mode Connections
- Common Misconceptions About Mean Median Mode Connections
- How to Calculate Mean Median Mode Connections
- Case Studies: Mean Median Mode Connections in Action
- Tools and Resources for Mastering Mean Median Mode Connections
- Challenges and Limitations of Mean Median Mode Connections
- Conclusion: Why Mean Median Mode Connections Are Essential