When you think about national grid, you're diving into a world where energy flows seamlessly from one corner of the country to another. It's not just wires and transformers; it's a lifeline that keeps our cities alive. Imagine a system so vast and intricate that it delivers electricity to millions of homes, businesses, and industries without missing a beat. That's the magic of the national grid, and today we're going to explore its inner workings, challenges, and the future it holds for us all.
The national grid is like the backbone of modern civilization. Without it, life as we know it would come to a screeching halt. Think about it – no lights, no internet, no air conditioning. Pretty crazy, right? The national grid ensures that power is distributed efficiently and reliably across vast distances, keeping everything running smoothly. But how does it work? What are the challenges it faces in today's rapidly changing energy landscape? Let's dive in and find out.
Now, before we get too technical, let me break it down for you. The national grid isn't just about electricity; it's also about innovation, sustainability, and resilience. It's a system that evolves with time, adapting to new technologies and addressing the growing demand for clean energy. Whether you're a homeowner, a business owner, or just someone curious about how the world works, understanding the national grid is key to grasping the future of energy. So, buckle up, because we're about to take a deep dive into the world of power grids!
Read also:The Mysterious Tale Of Thelma Todd Hollywoods Forgotten Star
What Exactly Is National Grid?
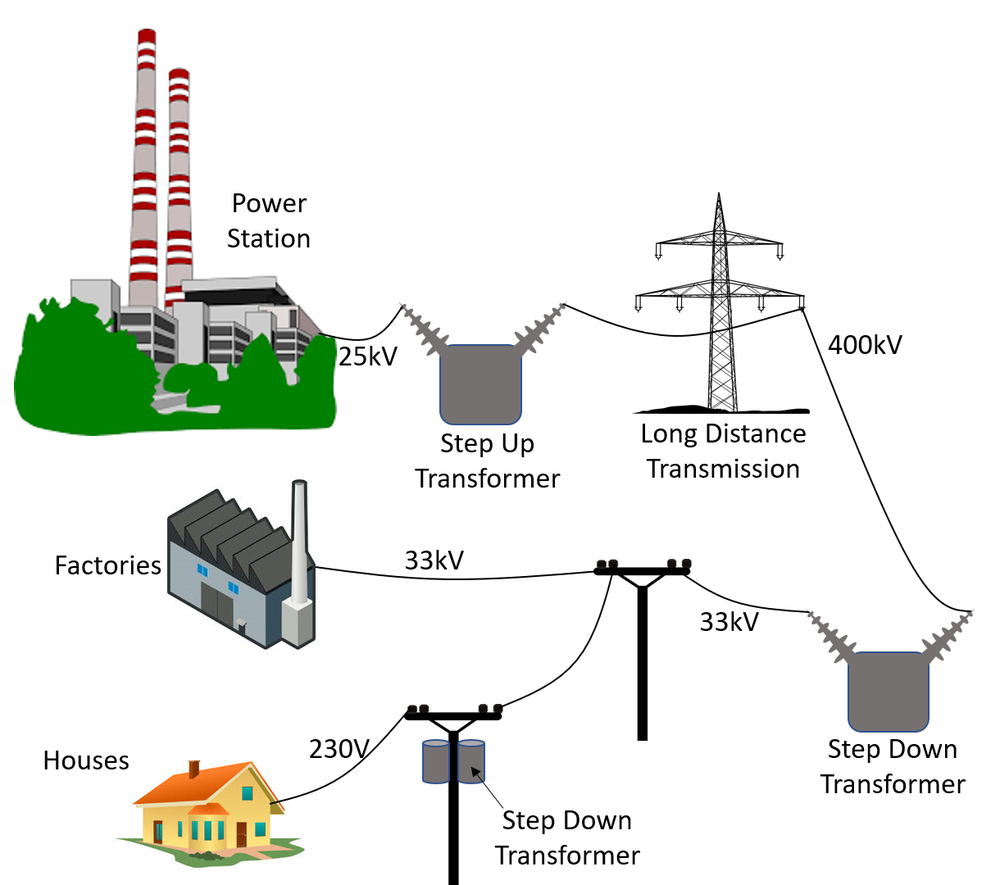
Let's start with the basics. The national grid is essentially a network of power lines, substations, and transformers that transmit electricity from power plants to consumers. It's a complex system that operates 24/7, ensuring that power is delivered where it's needed, when it's needed. Think of it as a highway for electricity, where power travels at lightning speed to keep our world running.
But here's the kicker: the national grid isn't just about transmitting electricity. It's also about balancing supply and demand. Imagine millions of people turning on their air conditioners on a hot summer day. The grid has to adjust instantly to meet that spike in demand without skipping a beat. It's like a symphony orchestra, where every component plays its part in perfect harmony.
Key Components of the National Grid
So, what makes up the national grid? Let's break it down into its key components:
- Power Plants: These are the generators that produce electricity. They can be fueled by coal, natural gas, nuclear energy, or renewable sources like wind and solar.
- Transmission Lines: These high-voltage lines carry electricity over long distances from power plants to substations.
- Substations: These are the points where voltage is stepped down for distribution to local areas.
- Distribution Lines: These lower-voltage lines deliver electricity to homes and businesses.
Each of these components plays a crucial role in ensuring that electricity flows smoothly from source to consumer. It's a well-oiled machine that operates behind the scenes, keeping our lives powered up.
History of the National Grid
The national grid as we know it today didn't just appear overnight. It has a rich history that dates back to the early 20th century. The first grids were small, localized systems that served specific areas. But as demand for electricity grew, so did the need for a more interconnected system.
In the 1920s and 1930s, countries like the United States and the United Kingdom began building large-scale grids to connect cities and rural areas. This was a game-changer, as it allowed for more efficient distribution of electricity and reduced the cost of power for consumers. Over the years, the grid has evolved, incorporating new technologies and adapting to changing energy needs.
Read also:American Idol Season 23 Carrie Underwood Joins As Judge Premiere Date And More
Milestones in Grid Development
Here are some key milestones in the development of the national grid:
- 1920s: The first large-scale grids are built in the US and UK.
- 1950s: The introduction of high-voltage transmission lines allows for more efficient long-distance power transmission.
- 1970s: The oil crisis leads to increased focus on energy efficiency and renewable energy sources.
- 2000s: Smart grid technology begins to emerge, enabling real-time monitoring and control of electricity flow.
Each of these milestones has played a significant role in shaping the national grid into the powerhouse it is today.
How Does the National Grid Work?
Now that we've covered the basics, let's dive deeper into how the national grid actually works. It's a complex system, but at its core, it's all about balancing supply and demand. Here's a step-by-step breakdown:
First, power is generated at power plants using various energy sources. This electricity is then transmitted through high-voltage lines to substations, where the voltage is stepped down for local distribution. From there, it travels through lower-voltage lines to homes and businesses, powering everything from lights to appliances.
But here's the tricky part: the grid has to constantly adjust to changes in demand. When people wake up in the morning and start using electricity, the grid responds by increasing supply. Similarly, when demand drops at night, the grid adjusts accordingly. It's a delicate balancing act that requires constant monitoring and control.
Grid Operations and Control
To manage this complex system, grid operators use advanced technologies like SCADA (Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition) systems. These systems provide real-time data on electricity flow, allowing operators to make instant adjustments as needed. It's like having a dashboard for the entire grid, where every component can be monitored and controlled remotely.
Additionally, the grid incorporates various safety mechanisms to prevent overloads and blackouts. Circuit breakers, for example, automatically cut off power when there's a surge, protecting equipment and ensuring the safety of consumers.
Challenges Facing the National Grid
While the national grid is an incredible feat of engineering, it's not without its challenges. As the world's energy needs continue to grow, the grid faces several pressing issues that need to be addressed.
One of the biggest challenges is aging infrastructure. Many parts of the grid were built decades ago and are in need of upgrades. This not only affects reliability but also increases the risk of failures and outages. Additionally, the rise of renewable energy sources like wind and solar presents new challenges in terms of integration and storage.
Solutions to Grid Challenges
So, how are these challenges being addressed? Here are some solutions that are being implemented:
- Grid Modernization: Upgrading infrastructure to improve reliability and efficiency.
- Renewable Integration: Developing technologies to better integrate renewable energy sources into the grid.
- Energy Storage: Investing in battery technology to store excess energy for use during peak demand.
These solutions are helping to create a more resilient and sustainable grid that can meet the energy needs of the future.
The Role of Technology in the National Grid
Technology is playing an increasingly important role in the evolution of the national grid. From smart meters to AI-driven analytics, new innovations are transforming the way electricity is generated, transmitted, and consumed.
Smart meters, for example, allow consumers to monitor their energy usage in real-time, helping them make more informed decisions about their energy consumption. AI and machine learning are being used to predict demand patterns and optimize grid operations, reducing the risk of outages and improving efficiency.
Emerging Technologies
Here are some emerging technologies that are shaping the future of the national grid:
- Smart Grids: Grids that use digital technology to monitor and manage electricity flow in real-time.
- Microgrids: Small-scale grids that can operate independently or in conjunction with the main grid, providing backup power during outages.
- Blockchain: A technology that could revolutionize energy trading and distribution by providing secure and transparent transactions.
These technologies are paving the way for a smarter, more efficient grid that can meet the challenges of the future.
The Future of the National Grid
Looking ahead, the national grid is poised for even more transformation. As the world shifts towards renewable energy and electric vehicles, the grid will need to adapt to accommodate these changes. This means investing in new technologies, upgrading infrastructure, and developing innovative solutions to ensure a reliable and sustainable energy supply.
One exciting development is the rise of decentralized energy systems, where power is generated closer to where it's consumed. This could reduce the need for long-distance transmission lines and make the grid more resilient to disruptions.
Trends to Watch
Here are some trends to watch in the future of the national grid:
- Increased Use of Renewables: As the cost of renewable energy continues to drop, we can expect to see more wind and solar farms connected to the grid.
- Electric Vehicles: The growing popularity of electric vehicles will drive demand for more charging stations and grid capacity.
- Energy Storage: Advances in battery technology will enable more efficient storage of excess energy, reducing the need for backup power plants.
These trends are shaping the future of the national grid and will play a crucial role in meeting the energy needs of tomorrow.
Conclusion
As we've explored in this article, the national grid is a vital component of modern life. It's a complex system that delivers electricity to millions of people every day, powering our homes, businesses, and industries. While it faces challenges, the grid is evolving to meet the demands of a changing world, incorporating new technologies and innovations to ensure a reliable and sustainable energy supply.
So, what can you do? First, stay informed about the latest developments in grid technology and renewable energy. Second, consider ways to reduce your energy consumption and support sustainable energy practices. And finally, share this article with your friends and family to spread awareness about the importance of the national grid.
Remember, the national grid is more than just wires and transformers; it's a lifeline that connects us all. By understanding how it works and supporting its evolution, we can help create a brighter, more sustainable future for generations to come.
Table of Contents
- What Exactly Is National Grid?
- History of the National Grid
- How Does the National Grid Work?
- Challenges Facing the National Grid
- The Role of Technology in the National Grid
- The Future of the National Grid